
Remove clothing around the site for easier access.

A severed artery is a medical emergency, because the muscular action of this blood vessel will pump the entire blood supply out of the wound in just a few minutes.įirst aid treatment for severe bleeding includes: Depending on the injury, underlying blood vessels can be punctured, leading to significant blood loss. Incised wounds are caused by sharp objects, such as knives or shards of glass, slicing into the skin. If you reapply antiseptic, wash it off after five minutes and then redress the wound.

Change the dressing according to the manufacturer’s instructions (some may be left in place for several days to a week).Cover the cleaned wound with an appropriate non-stick sterile dressing.Don’t scrub at embedded dirt, as this can traumatise the site even more.Rinse the wound after five minutes with sterile saline or flowing tap water. If there is embedded dirt, Savlon may be used as it contains an antiseptic and a surfactant to help remove debris. Clean the wound with a non-fibre shedding material or sterile gauze, and use an antiseptic such as Betadine.
Coloring page layers of the skin skin#
The scraped skin of an abrasion can contain particles of dirt. Thin-skinned bony areas (like knees, ankles and elbows) are more prone to abrasions than thicker, more padded areas. First aid for abrasionsĪn abrasion means that the surface layers of the skin (epidermis) has been broken. The two broad categories of skin wounds include abrasions and incised wounds.
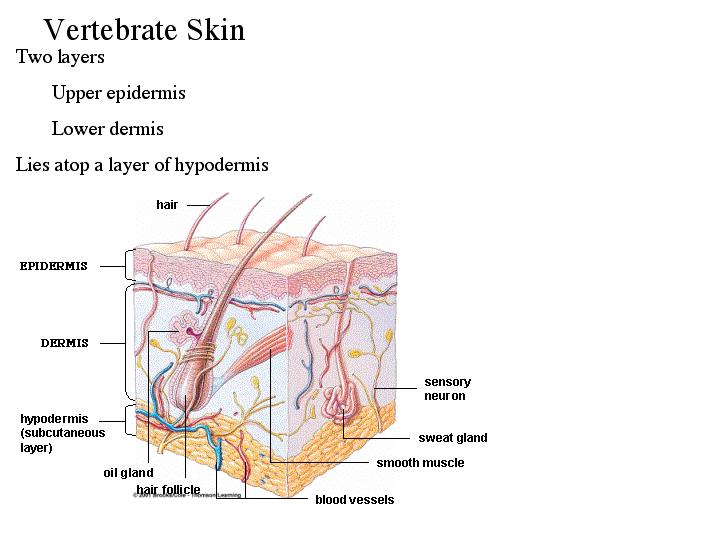
Sebaceous glands, hair follicles, nerves and blood vessels are found in the dermis. The dermis lies underneath and consists of elastic fibres (elastin), for suppleness, and protein fibres (collagen) for strength. The epidermis refers to the surface layer and is made of several sheets of skin cells. It consists of two main layers – the epidermis and the dermis. It varies in texture and thickness from one part of the body to the next. It is soft to allow movement, but tough enough to resist breaking or tearing. Skin is the largest organ of the human body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
